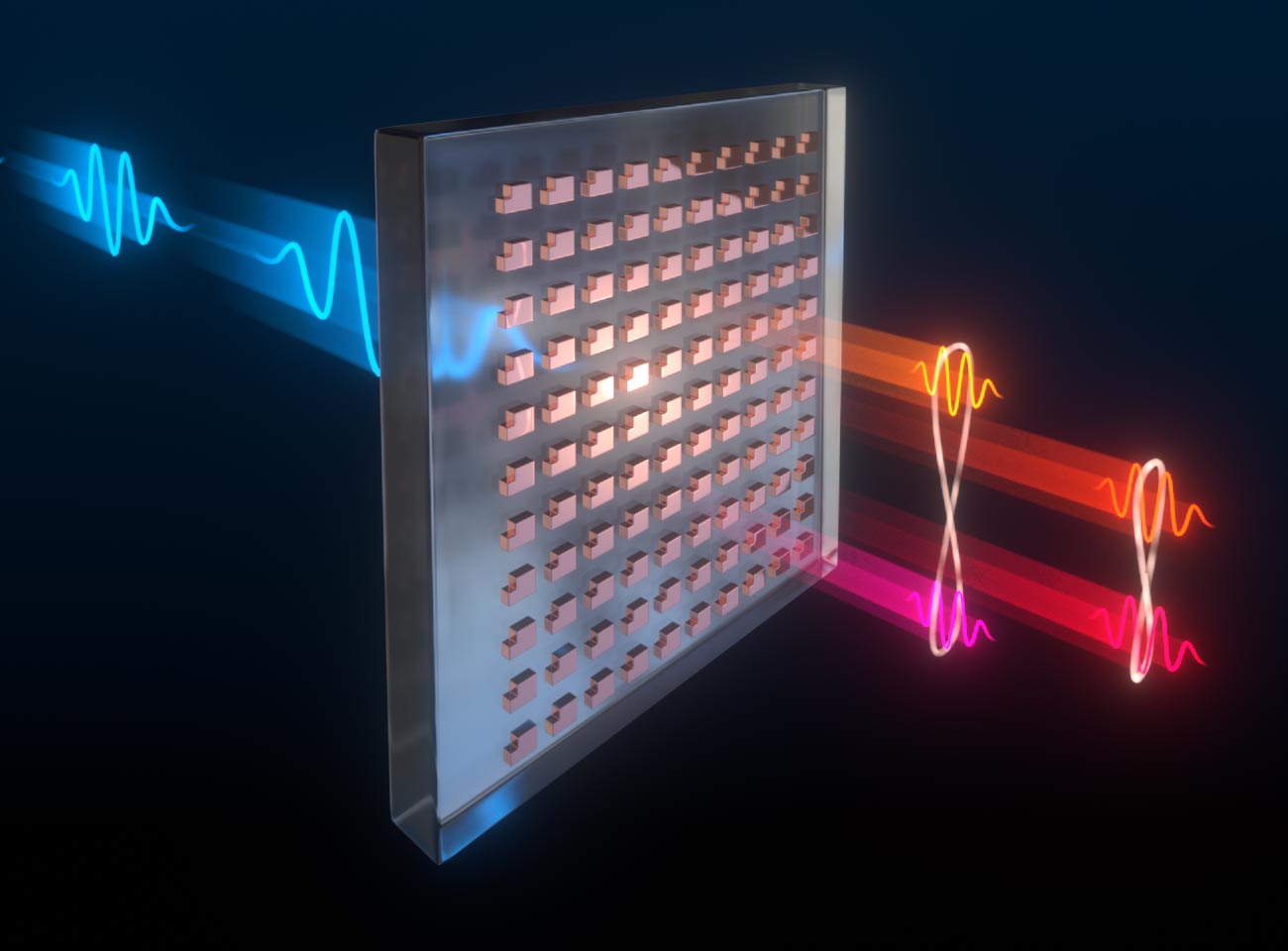
في عرض هذا الفنان للسطح الخارق ، يمر الضوء من خلال هياكل مستطيلة دقيقة – اللبنات الأساسية للسطح الخارق – ويخلق أزواجًا من الفوتونات المتشابكة بأطوال موجية مختلفة. تم تصميم الجهاز وتصنيعه واختباره من خلال شراكة بين مختبرات سانديا الوطنية ومعهد ماكس بلانك لعلوم الضوء. الائتمان: بإذن من إيغال برينر ، مختبرات سانديا الوطنية
من خلال المرآة الكمومية
من خلال مساعدة العلماء على التحكم في ظاهرة غريبة ولكنها مفيدة لميكانيكا الكم ، يمكن للاختراع الرقيق للغاية أن يجعل تقنيات الحوسبة والاستشعار والتشفير المستقبلية أصغر حجمًا وأكثر قوة بشكل ملحوظ. الجهاز موصوف في بحث جديد نشر مؤخرا في المجلة العلم.
وفقًا لعلماء من مختبرات سانديا الوطنية ومعهد ماكس بلانك لعلوم الضوء ، يمكن لهذا الجهاز أن يحل محل غرفة مليئة بالمعدات لربط الفوتونات معًا في تأثير كمي غريب يسمى التشابك. إنه نوع من المواد المصممة بالنانو تسمى السطح الخارق ويمهد الطريق لتشابك الفوتون بطرق معقدة لم تكن ممكنة باستخدام التقنيات المدمجة.
عندما يقال إن الفوتونات متشابكة ، فهذا يعني أنها مرتبطة بطريقة تؤثر فيها الإجراءات على الآخر ، بغض النظر عن مكان أو مدى تباعد الفوتونات في الكون. إنه تأثير مخيف لميكانيكا الكم وقوانين الفيزياء التي تحكم الجسيمات والأشياء الصغيرة الأخرى.

يضيء ضوء الليزر الأخضر سطحًا خارقًا أرق مائة مرة من الورق ، الذي تم تصنيعه في مركز تقنية النانو المتكاملة. يتم تشغيل CINT بشكل مشترك من قبل مختبرات سانديا ولوس ألاموس الوطنية لإدارة الطاقة ، مكتب العلوم. الائتمان: كريج فريتز ، مختبرات سانديا الوطنية
على الرغم من أن هذه الظاهرة قد تبدو غريبة ، فقد استغلها الباحثون لمعالجة المعلومات بطرق جديدة. على سبيل المثال ، يساعد التشابك في حماية المعلومات الكمية الدقيقة وتصحيح الأخطاء في[{” attribute=””>quantum computing, a field that may someday have sweeping impacts on science, finance, and national security. Entanglement is also enabling advanced new encryption methods for secure communication.
Research for the groundbreaking device, which is a hundred times thinner than a sheet of paper, was conducted, in part, at the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies, a Department of Energy Office of Science user facility operated by Sandia and Los Alamos national laboratories. Sandia’s team received funding from the Office of Science, Basic Energy Sciences program.
Light goes in, entangled photons come out
The new metasurface acts as a portal to this unusual quantum phenomenon. In some ways, it’s like the mirror in Lewis Carroll’s “Through the Looking-Glass,” through which the young protagonist Alice experiences a strange, new world.
Instead of walking through their new device, scientists shine a laser through it. The beam of light passes through an ultrathin sample of glass covered in nanoscale structures made of a common semiconductor material called gallium arsenide.
“It scrambles all the optical fields,” said Sandia senior scientist Igal Brener. He is an expert in a field called nonlinear optics and led the Sandia team. Occasionally, he said, a pair of entangled photons at different wavelengths emerge from the sample in the same direction as the incoming laser beam.

Sandia National Laboratories senior scientist Igal Brener, an expert in nonlinear optics, led a team that helped demonstrate a device that is paving the way for powerful, compact quantum information processing technologies. Credit: Craig Fritz, Sandia National Laboratories
Brener said he is enthusiastic about this device because it is designed to produce complex webs of entangled photons. Instead of just one pair at a time, it can produce several pairs all entangled together, and some that can be indistinguishable from each other. Some technologies require these complex varieties of so-called multi-entanglement for sophisticated information processing schemes.
Although other miniature technologies based on silicon photonics can also entangle photons, they lack the much-needed level of complex, multi-entanglement. Until now, the only way to produce such results was with multiple tables full of lasers, specialized crystals, and other optical equipment.
“It is quite complicated and kind of intractable when this multi-entanglement needs more than two or three pairs,” Brener said. “These nonlinear metasurfaces essentially achieve this task in one sample when before it would have required incredibly complex optical setups.”
The Science paper outlines how the team successfully tuned their metasurface to produce entangled photons with varying wavelengths. This was a critical precursor to generating several pairs of intricately entangled photons simultaneously.
However, the scientists note in their paper that the efficiency of their device — the rate at which they can generate groups of entangled photons — is lower than that of other techniques and will need to be improved.
What is a metasurface?
A metasurface is a synthetic material that interacts with light and other electromagnetic waves in ways conventional materials can’t. Brener said that commercial industries are busy developing metasurfaces because they take up less space and can do more with light than, for instance, a traditional lens.
“You now can replace lenses and thick optical elements with metasurfaces,” Brener said. “Those types of metasurfaces will revolutionize consumer products.”
Sandia is one of the leading institutions in the world performing research in metasurfaces and metamaterials. Between its Microsystems Engineering, Science and Applications complex, which manufactures compound semiconductors, and the nearby Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies, scientists have access to all the specialized tools they need to design, fabricate, and analyze these ambitious new materials.
“The work was challenging as it required precise nanofabrication technology to obtain the sharp, narrowband optical resonances that seed the quantum process of the work,” said Sylvain Gennaro, a former postdoctoral researcher at Sandia who worked on several aspects of the project.
The device was designed, fabricated, and tested through a partnership between Sandia and a research group led by physicist Maria Chekhova. She is an expert in the quantum entanglement of photons at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light.
“Metasurfaces are leading to a paradigm shift in quantum optics, combining ultrasmall sources of quantum light with far-reaching possibilities for quantum state engineering,” said Tomás Santiago-Cruz. He is a member of the Max Plank team and first author on the paper.
Brener, who has studied metamaterials for more than a decade, said this newest research could possibly spark a second revolution — one that sees these materials developed not just as a new kind of lens, but as a technology for quantum information processing and other new applications.
“There was one wave with metasurfaces that is already well established and on its way. Maybe there is a second wave of innovative applications coming,” he said.
Reference: “Resonant metasurfaces for generating complex quantum states” by Tomás Santiago-Cruz, Sylvain D. Gennaro, Oleg Mitrofanov, Sadhvikas Addamane, John Reno, Igal Brener and Maria V. Chekhova, 25 August 2022, Science.
DOI: 10.1126/science.abq8684



